Description
Healgen Scientific Adulteration AD Test Strips, 25/Bottle
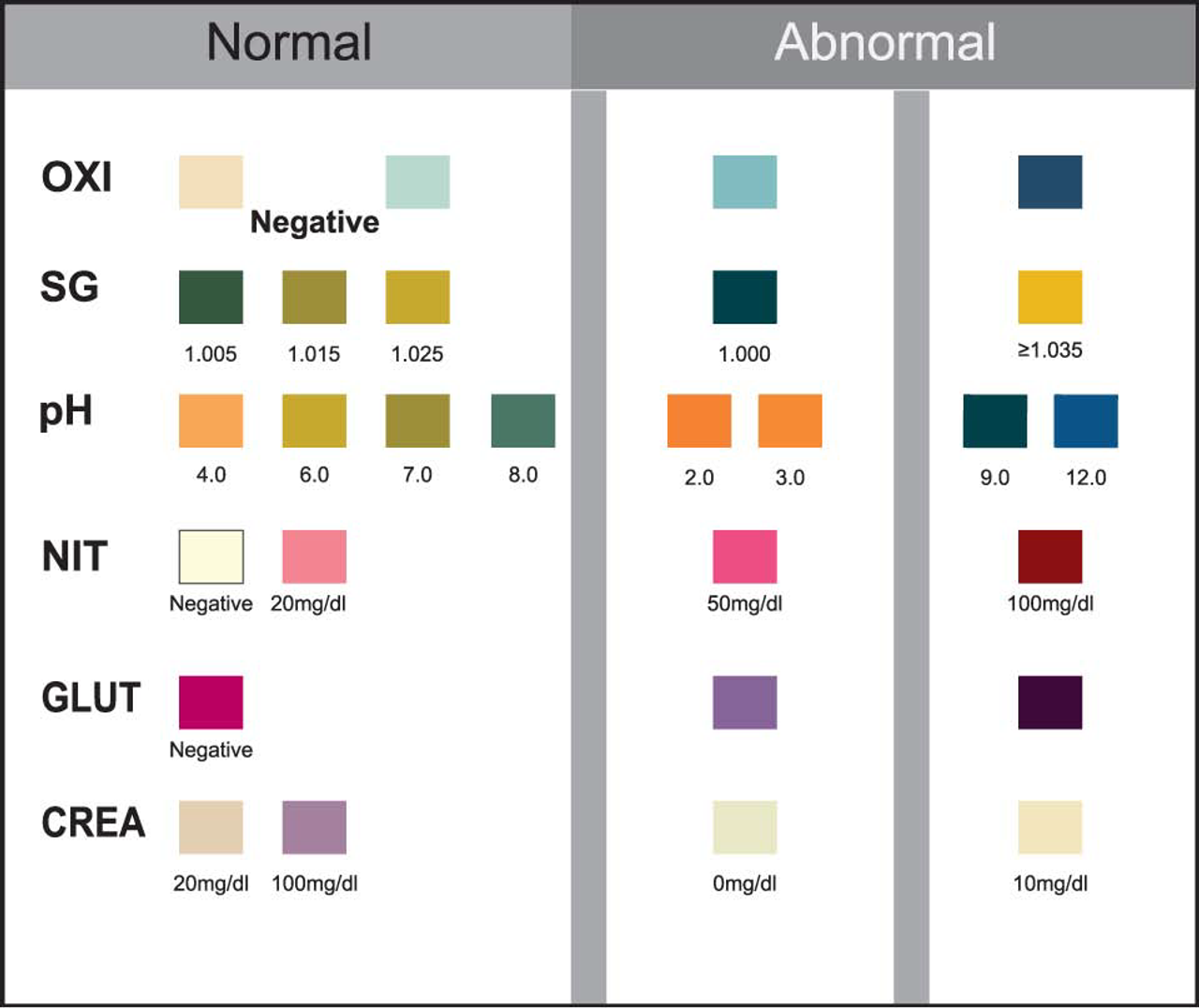
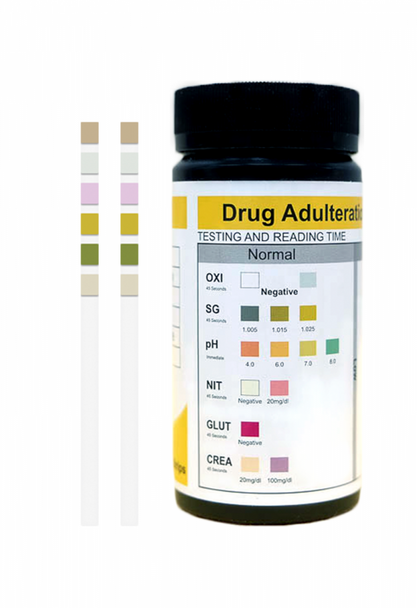
Urine reagent test strips for Adulteration is a screening test device for the visual qualitative determination of creatinine, nitrite, glutaraldehyde, pH, specific gravity, and oxidents/pyridinium chlorochromate in urine, it does not indicate the level or concentrations of compounds present in the sample. Results in one minute.
- Oxidants/Pyridinium (PCC)
- Specific Gravity
- pH
- Nitrite
- Glutaraldehyde
- Creatinine
SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION
The validity of DAU screening depends on the integrity of the urine samples. Contaminated or adulterated samples may cause erroneous results leading to significant consequences. Hence, it is important to ensure that the samples are intact and consistent with normal human urine.
The urine adulteration test strips are plastic strips affixed with seven reagent pads. The pads are chemically treated with specific reagents to provide visual comparison of these pads with the color chart on the container label after dipping the test strip into a urine sample, the following information can be obtained which may be useful in assessing the integrity of the urine sample:
- Whether the sample is diluted or substituted with water or other liquids as indicated by the creatinine and specific gravity tests
- Whether the sample contains commercially available adulterants including nitrite3 “KLEAR”, glutaraldehyde4, bleach, pyridinium chlorochromate “Insta Clean ADD-IT-IVE”, “LUCKY LAB”, and other oxidizing agents “STEALTH”, “Urine Luck”
- Whether the sample is contaminated with common household items, such vinegar, Drano, Hydrogen Peroxide and Bleach as indicated by the pH, Bleach and Pyridinium Chlorochromate tests
DOWNLOAD REFERENCE DOCUMENTS
 Intect 7 Adulterant Test Strips Package Insert
Intect 7 Adulterant Test Strips Package Insert
| ADULTERANTS PANELS | |
| Creatinine | In this assay, creatinine reacts with a creatinine indicator in an alkaline medium to form a purplebrown color complex. The color intensity of the test pad is directly proportional to the concentration of creatinine in the sample. Daily creatinine excretion, related to muscle mass of the human body, is usually constant. Urine specimens with creatinine levels of less than 20 mg/dl are indications of adulteration. This test covers the most common form of specimen tampering, specimen dilution. Dilution using diuretics is also often referred to as “flushing”. |
| Glutaraldehyde | This analysis is based on the reaction of the aldehyde group on the glutaraldehyde with an indicator to generate a brown color complex. Tests for the presence of exogenous aldehyde. Glutaraldehyde is not a natural component of human urine and it should not be present in normal urine. Common occurrences are the additives of such products such as Clear Choice or UrinAid. |
| Nitrite | Test for the presence of diazo-compound. This test is based on the reaction of aromatic amine to yield a diazonium salt which then couples with an indicator to form a color complex ranging from pink to dark red depending on the concentration of nitrite in the sample. Nitrite level above 50mg/dl is considered abnormal. Common occurrences are the additive of such products as Klear. |
| Oxidants | Testing for presence of oxidizing reagents. In this reaction, a color indicator reacts with oxidants such as bleach, hydrogen peroxide or pyridinium chlorochromate to form a blue or green color . The presence of high levels of antioxidants in the specimen, such as ascorbic acid, may result in false negative results for the oxidant pad. And the formation of blue pad color may also indicate the presence of other oxidative adulterants |
| pH Level | This test utilizes the principle of multiple indicators that give a broad range of colors ranging from orange (low pH) to yellow and green (pH 4 to 9) and brown (high pH). Tests for the presence of acidic and alkaline adulterants. Normal urine pH ranges from 4.0 to 9.0. Values below pH 4.0 or above pH 9.0 are indicative of adulteration. |
| Specific Gravity | Testing for sample dilution. Normal levels for specific gravity will range from 1.003-1.030. Specific gravity levels of less than 1.003 or higher than 1.030 are indication of adulteration. In the presence of an indicator, the colors range from dark blue or blue green in urine of low ionic concentration to green and yellow in urine of higher ionic concentration. Elevated levels of protein in urine may cause specific gravity values to be higher. |
Compare each reagent area to its corresponding color blocks on the color chart printed on the bottle and read at the times specified.