Description
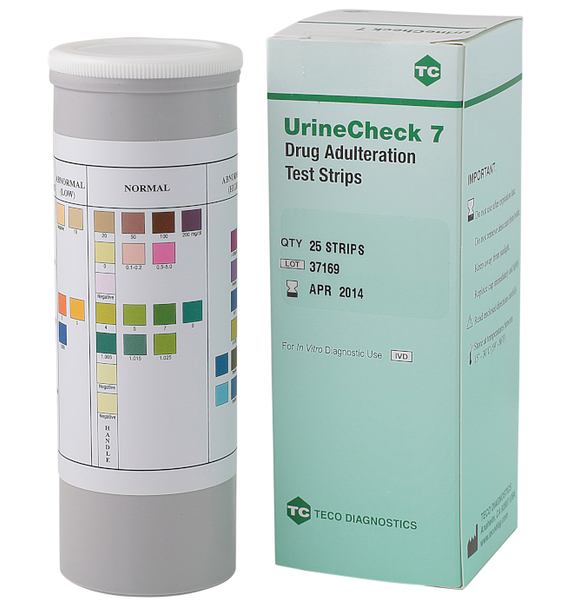
UrineCheck 7 Adulteration Test Strips
The UrineCheck 7 Adulteration Test Strips tests urine specimens for Creatinine, Glutaraldehyde, Nitrite, Oxidants, pH, Bleach, and Pyridinium Chlorochromate levels. The test strip is used to determine specimen urine integrity. If the sample is out of normal range, then the sample is considered adultered and not valid.
These Drug Adulteration Strips are a fast dip-and-read test for the determination of diluted or adulterated urine specimens. Adulteration is the intentional manipulation of urine sample in order to pass a drug screening test. The seven-in one test strips are based on the chemical reactions of the indicator reagents on the pads with components in the urine sample effecting color changes.
INTENDED USE
UrineCheck 7 is a fast dip-and-read test for the determination of diluted or adulterated urine specimens. It is an important pre-screening test for any drug-testing program.
SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION
UrineCheck 7 drug adulteration tests are firm plastic strips to which seven different reagent areas are affixed. UrineCheck 7 test strips are ready-to-use and disposable. No equipment is required for its use. Only fresh and uncentrifuged urine samples without preservatives are to be used. UrineCheck 7 provides tests for Creatinine, Nitrite, pH, Specific Gravity, Glutaraldehyde, Bleach, and Pyridinium Chlorochromate in urine. Test results may be useful for assessing the integrity of the urine sample prior to Drugs-of-Abuse testing.
For example, whether the sample is possibly diluted with water or other liquids as indicated by the creatinine and specific gravity tests. UrineCheck 7 detects whether the sample contains commercially available adulterants including nitrite, glutaraldehyde, bleach, pyridinium chlorochromate and other oxidizing agents. UrineCheck 7 can also assess whether the sample is possibly contaminated by acidic (vinegar) or basic (ammonia solution) adulterants as indicated by the pH test.
Creatinine: Testing for sample dilution. In this assay, creatinine reacts with a creatinine indicator under alkaline conditions to form a purplish-brown color complex. The concentration of creatinine is directly proportional to the color intensity of the test pad.
Glutaraldehyde: Testing for the presence of exogenous aldehyde. In this assay, the aldehyde group on the glutaraldehyde reacts with an indicator to form a pink color complex.
Nitrite: Testing for the presence of exogenous nitrite. Nitrite reacts with an aromatic amine to form a diazonium compound in an acid medium. The diazonium compound, in turn, couples with an indicator to produce a pink-red color
Oxidants: Testing for the presence of oxidizing reagents. In this reaction, a color indicator reacts with oxidants such as bleach, hydrogen peroxide or pyridinium chlorochromate to form a blue color complex. Other colors may indicate the presence of other oxidants.
pH Level: Testing for the presence of acidic or alkaline adulterant. This test is based on the well-known double pH indicator method that gives distinguishable colors over a wide pH range. The colors range from orange (low pH) to yellow and green to blue (high pH). Specific Gravity: Testing for sample dilution. This test is based on the apparent pKa change of certain pretreated polyelectrolytes in relation to the ionic concentration. In the presence of an indicator, the colors range from dark blue or blue-green in urine of low ionic concentration to green and yellow in urine of higher ionic concentration
Bleach: Testing for the presence of bleach in urine. In this test, the presence of bleach forms a blue-green, brown, or orange color complex.
Pyridinium Chlorochromate: Testing for the presence of Pyridinium chlorochromate in urine. In this test, the presence of chromate forms a blue-green color complex.